The same version of Windows is sold in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. Previously, the 32-bit version was the mainstream, but the 64-bit version has become the mainstream lately.
This article provides you with how to find out if you have a 32-bit or 64-bit OS or applications, using Windows 10, macOS, and Excel (for Windows and Mac) as examples. You can also learn about bit and byte that frequently appear in the computer world.
–
1. How to check on Window10
1 Click the Start button and then click Settings.
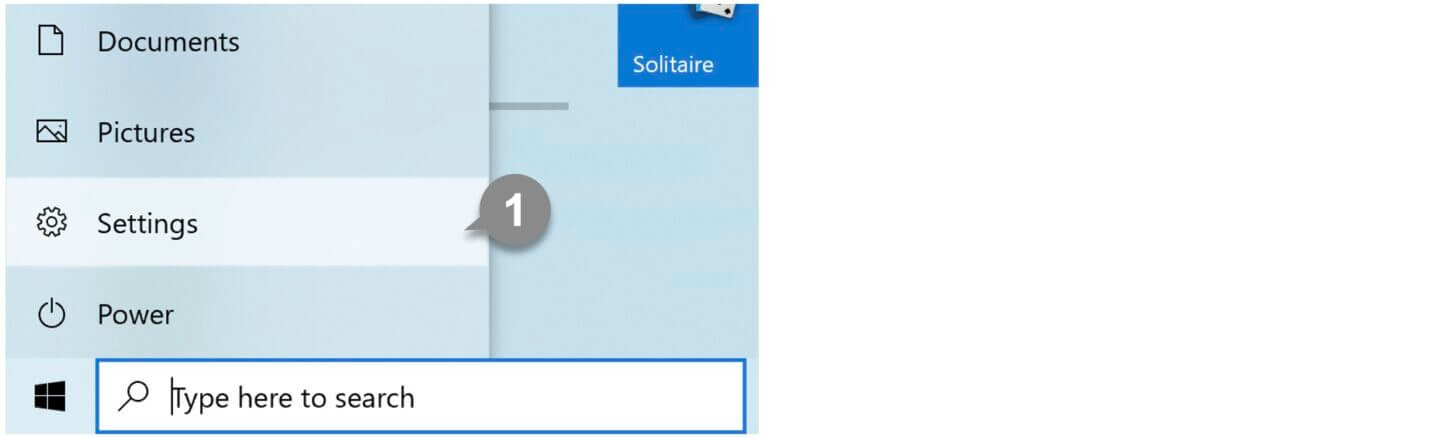
2 Click System on the Settings dialog box.
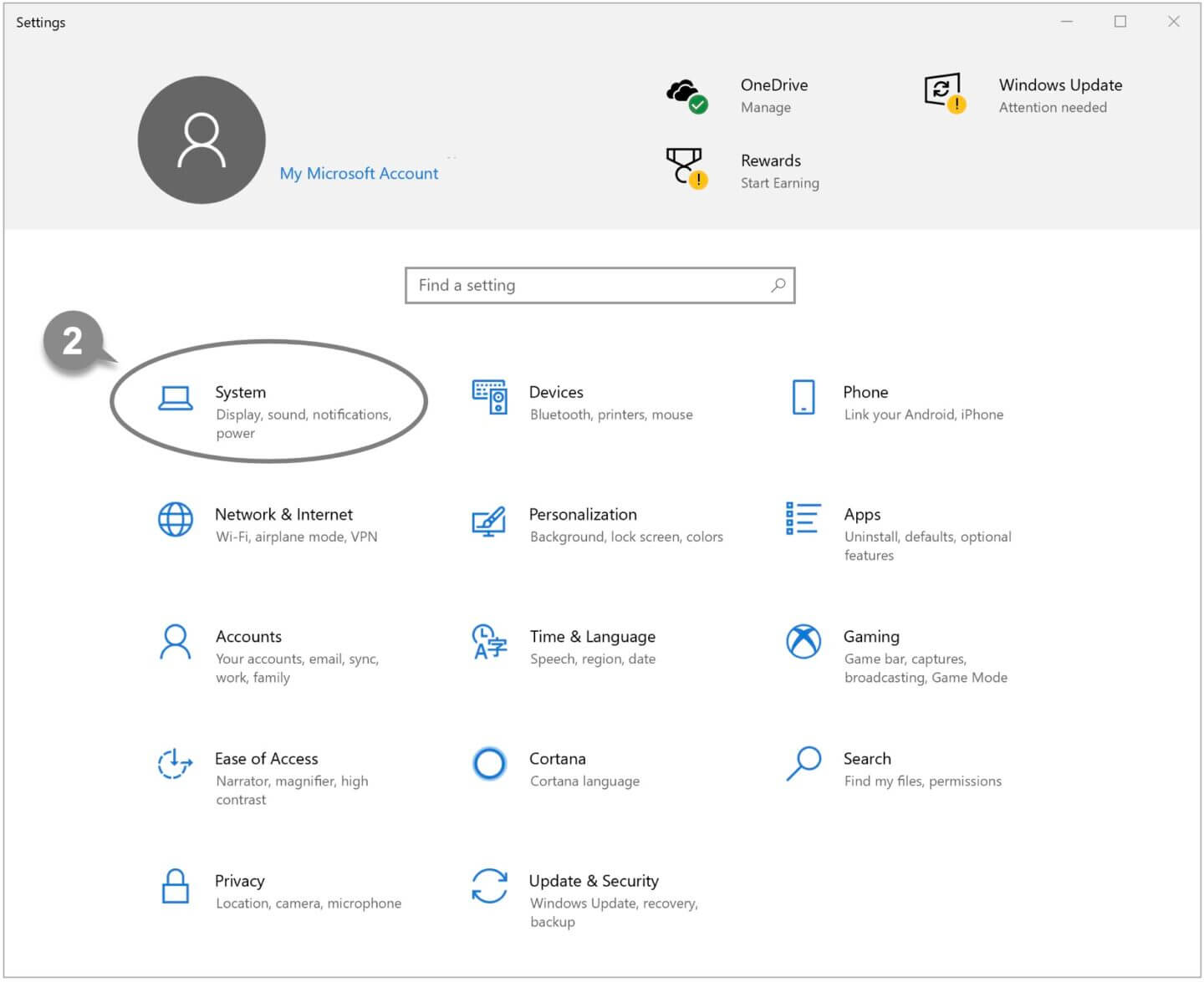
3 Click About on the left side of the screen.
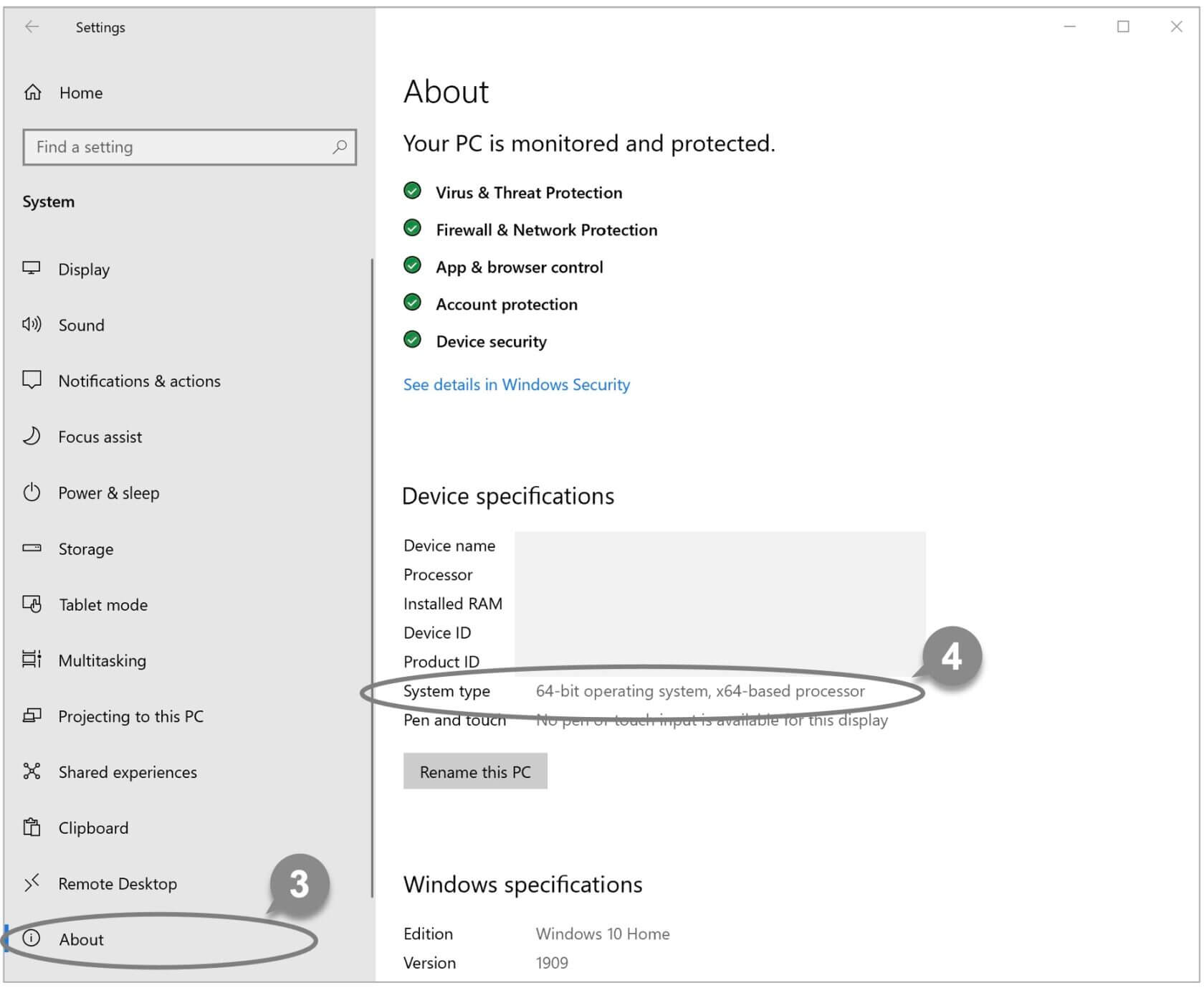
4 Under System type, you can find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
2. How to check on MacOS
On a Mac, an Intel-based processor identifies whether the OS is 32-bit or 64-bit.
1 Click About This Mac on the Apple menu.
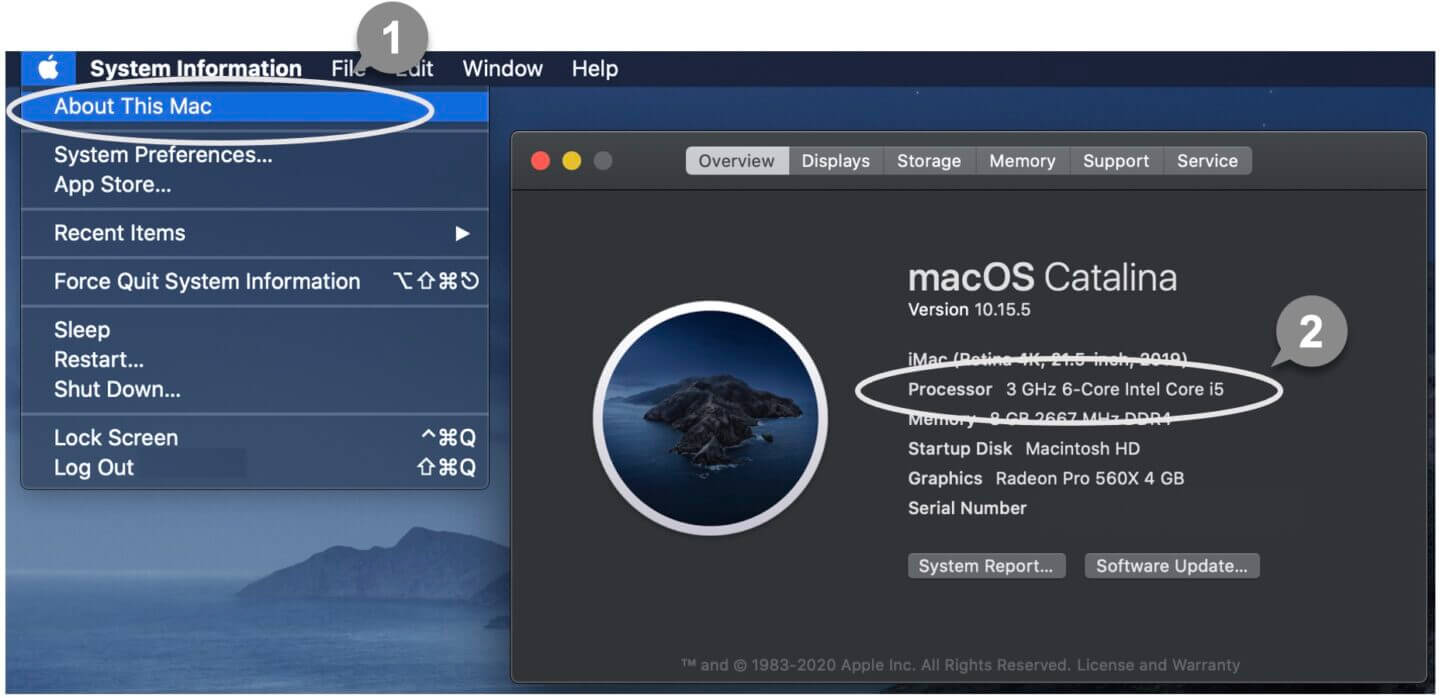
2 View the Processor Name.
3 Check your Processor Name to the information below to find out whether your Mac has a 32-bit or 64-bit processor.
| Processor Name | 32-bit / 64-bit |
|---|---|
| Intel Core Solo | 32 bit |
| Intel Core Duo | 32 bit |
| Intel Core 2 Duo | 64 bit |
| Intel Quad-Core Xeon | 64 bit |
| Dual-Core Intel Xeon | 64 bit |
| Quad-Core Intel Xeon | 64 bit |
| Core i3 | 64 bit |
| Core i5 | 64 bit |
| Core i7 | 64 bit |
–
3. How to check on Excel for Windows
1 Run Excel.
2 Click Account on the left side of the screen, then click the About Excel button on the right side of the screen.
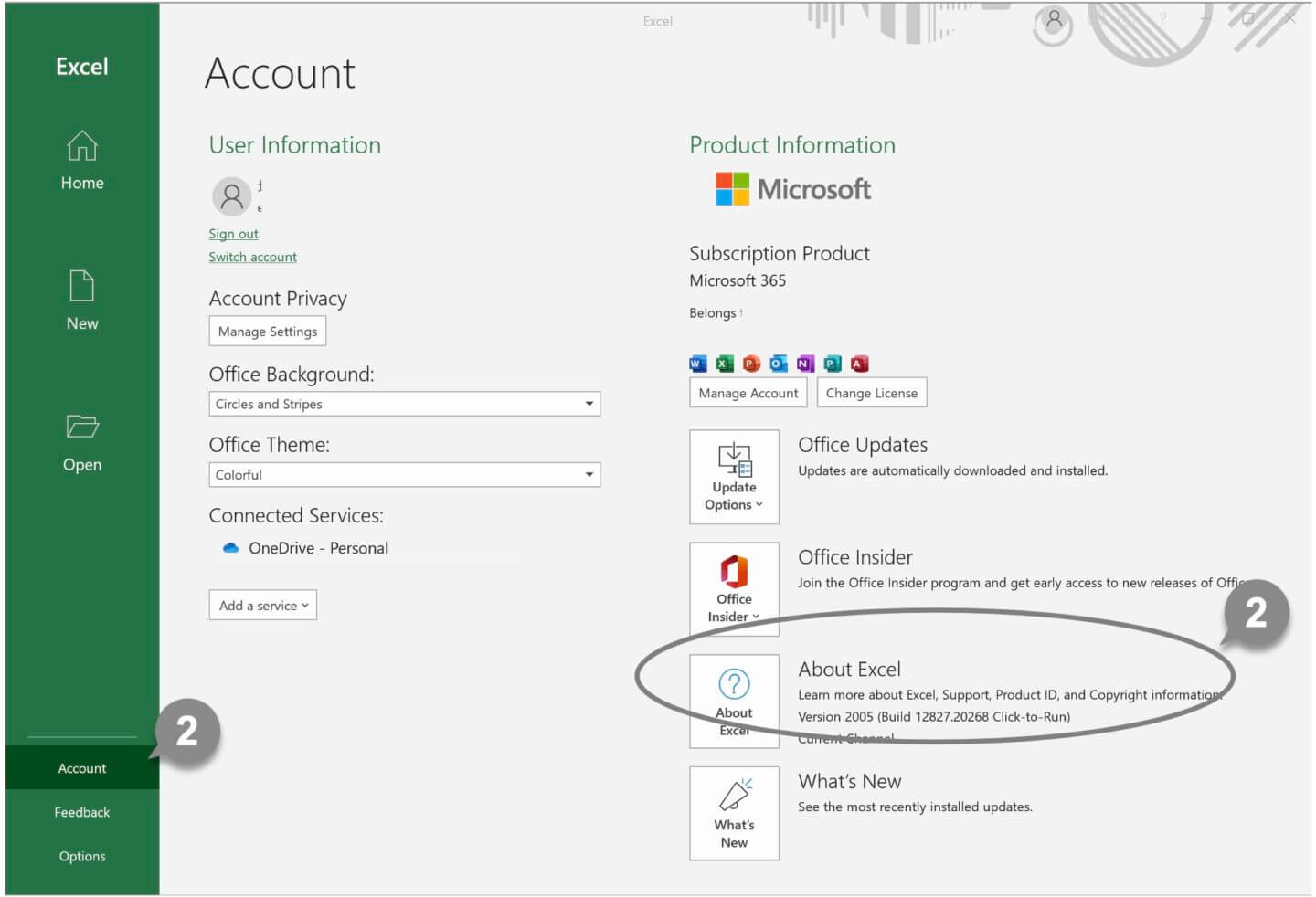
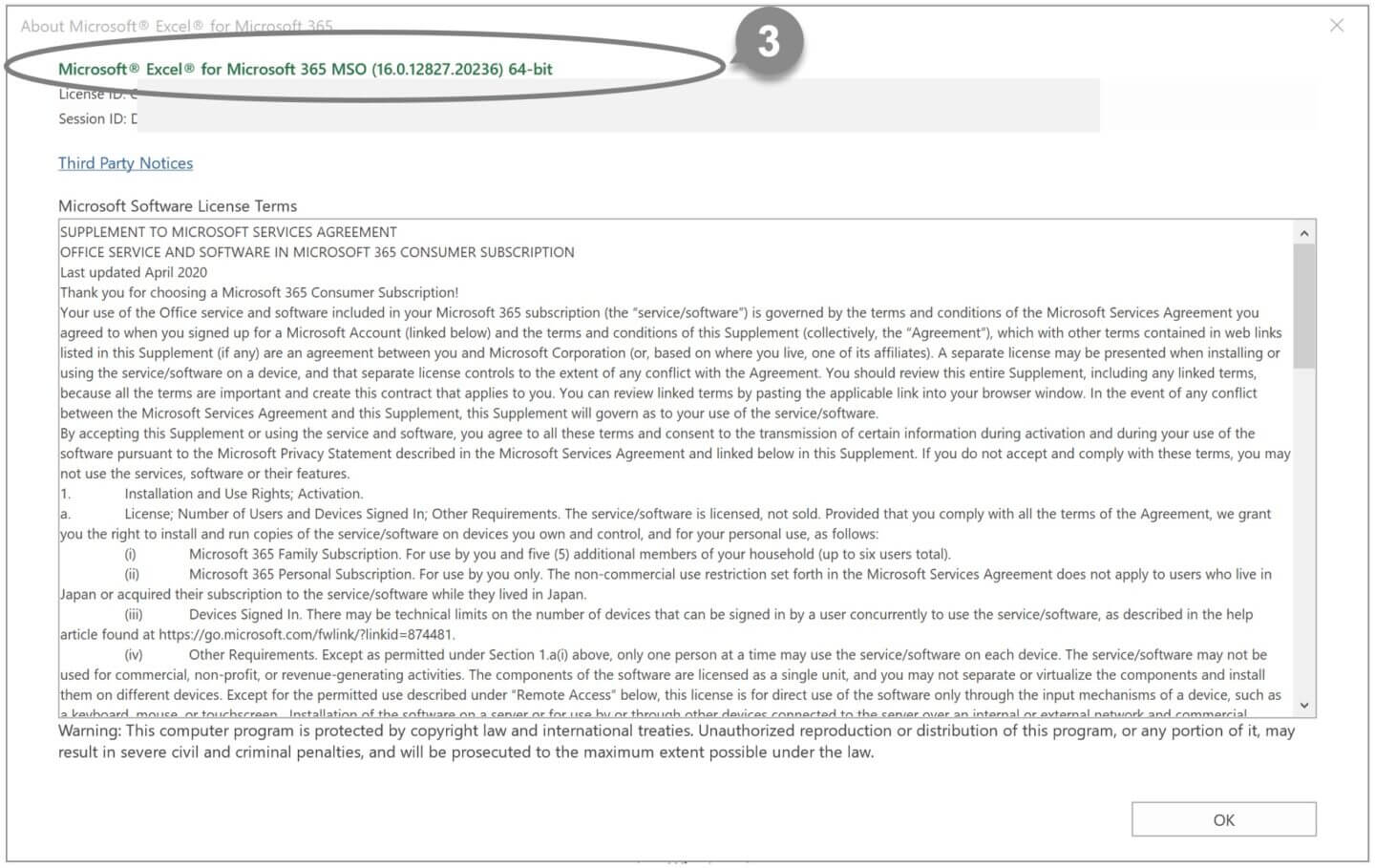
3 You can find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Excel in the following dialog box.
4. How to check on Excel for Mac
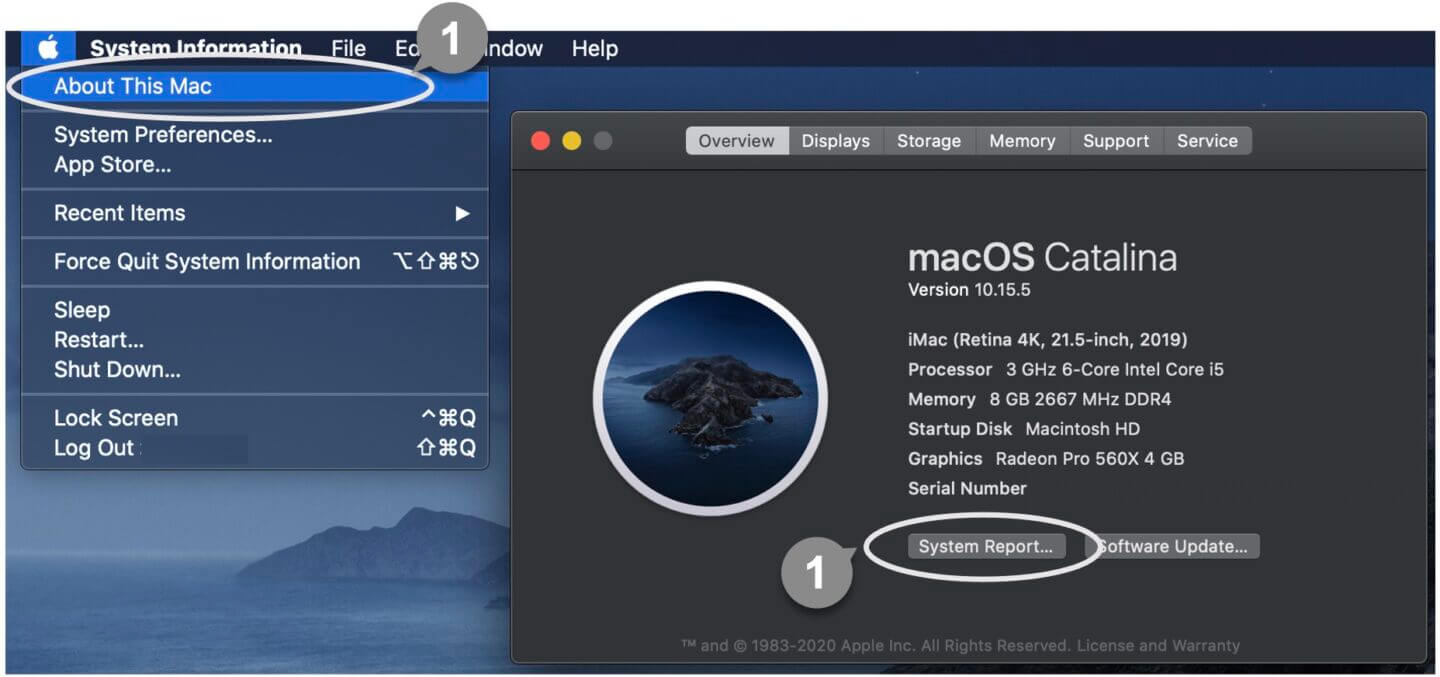
1 Click About This Mac on the Apple menu, then click System Report.
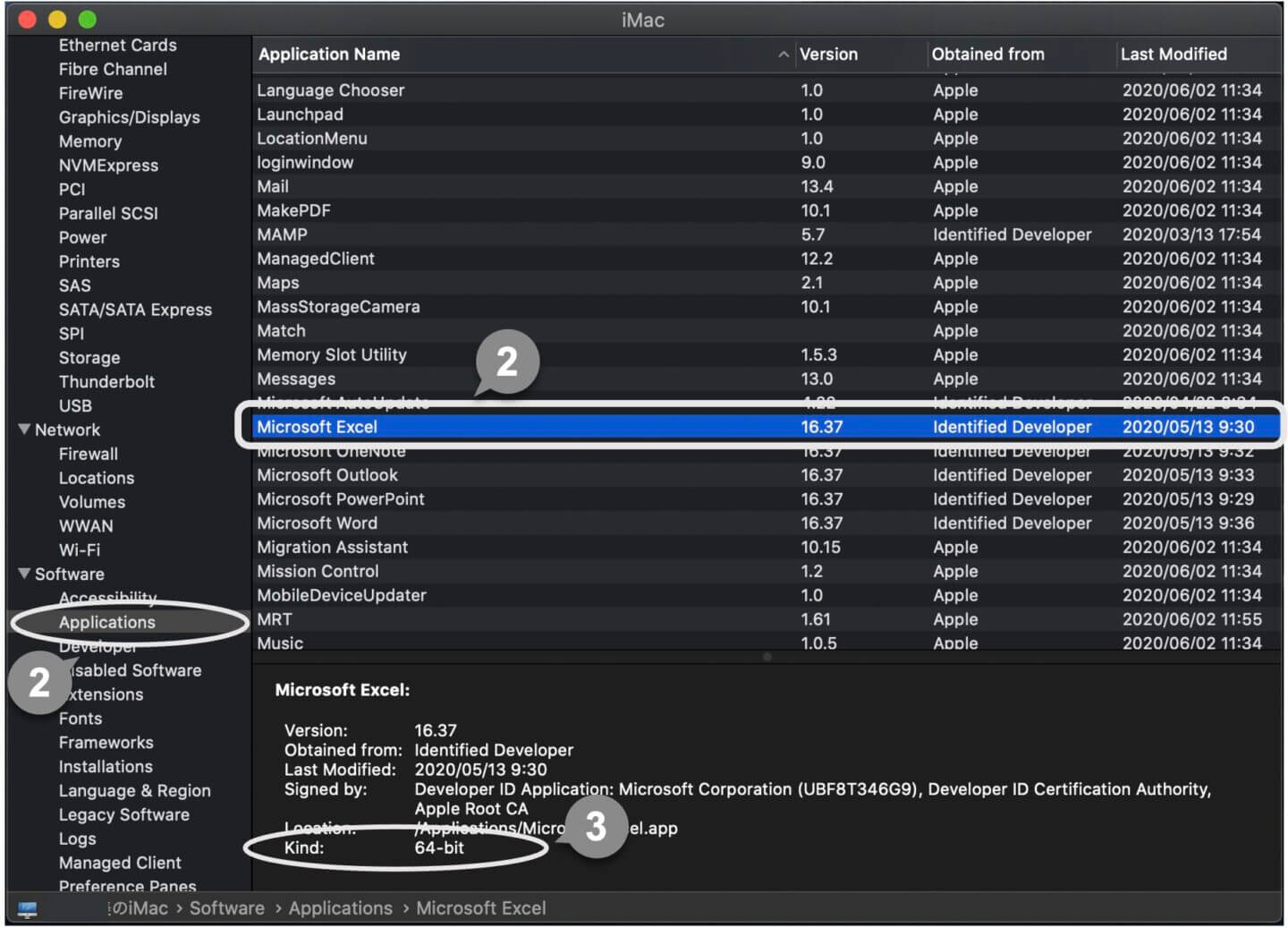
2 Under the software group, select Applications on the left side of the screen, then select Microsoft Excel from the list on the right side of the screen.
3 Under Kind, you can find out whether you have a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Excel.
5. Bit and Byte
The terms of bit and byte come up a lot in computers. This is a unit used to describe the size of the data. In our daily life, we use decimal numbers such as 0, 1, 2, 3, 4… 9, but computers use binary numbers to represent all data as a combination of 0 and 1.
Convert from decimal to binary
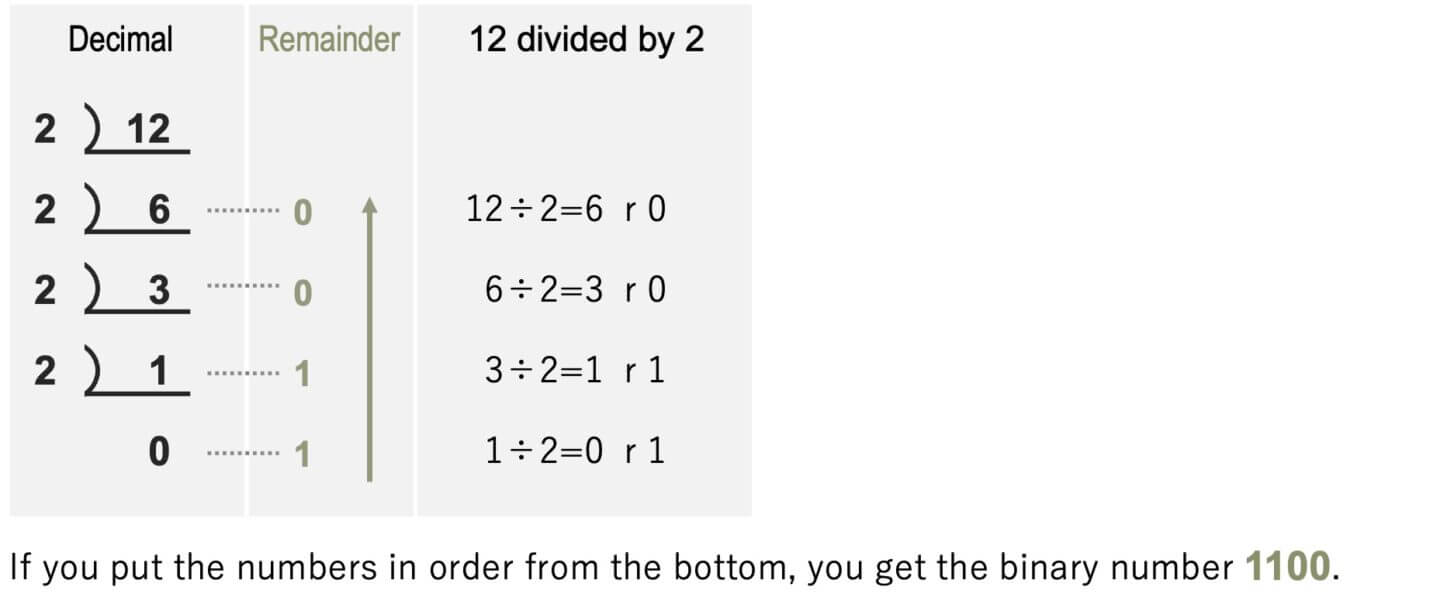
Convert from binary to decimal

Computers can do very complex things, but the basic mechanism is that current is either flowing or not flowing in the electronic circuitry, and they process things in these two states. The OFF state that no current is flowing is set to [ 0 ], and the ON state that current is flowing is set to [ 1 ]. All data entered into computer is converted into numbers of 0 and 1 and further processed by replacing them with ON and OFF electrical signals. The unit for representing the data in two ways, OFF [ 0 ] or ON [ 1 ], is called ” Bit “. Bit stands for binary digit and is the smallest unit of data handled by a computer.
The combination of 0 and 1 is increasing, such as 1 digit for 1 bit and 2 digits for 2 bits. The larger the number of bits, the more information it can handle. Byte is a unit of information that consists of 8 bits. 1 byte has eight 0s to 1s in a row, and 256 ways (2 to the 8th power) of data can be represented.
| 1-bit | 0, 1 ( 1 digit, 2 ways combination = 1 square of 2 ) |
| 2-bit | 00, 01, 10, 11 ( 2 digits, 4 ways combination = 2 squared ) |
| 8-bit | 00000000, 00000001,…(8 digits, 256 ways combination = 2 to the 8th power) |
What is CPU?
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, it receives data from input devices such as mouse and keyboard, and storage devices such as memory and hard disks to calculate and control the movement of other devices. In humans, it is the equivalent of the brain or central nervous system. You may have also seen and heard terms like 32-bit CPU and 64-bit CPU. The 32-bit and 64-bit values indicate the amount of data that the CPU’s data transmission channel can send at one time, and the larger the number of bits, the more data the CPU can read and process.
The 32-bit CPU
- 32 data transmission channels
- 2 to the 32nd power = 4 GB (about 4.3 billion bytes)
- Theoretically, it can handle up to 4GB of memory
The 64-bit CPU
- 64 data transmission channels
- 2 to the 64th power = 16EB (about 17.2 billion GB)
- Theoretically, it can handle up to 17.2 billion GB of memory
SI Prefixes
The amount of data that can be handled by PC is increasing as the performance improves. Therefore, we use a combination of auxiliary units to express a large amount of data in an easy-to-understand manner.

–
